Rotating Black Hole Schwarzschild Radius Schwarzschild Metric Event
New formula for calculating Hawking radiation at the event horizon of a

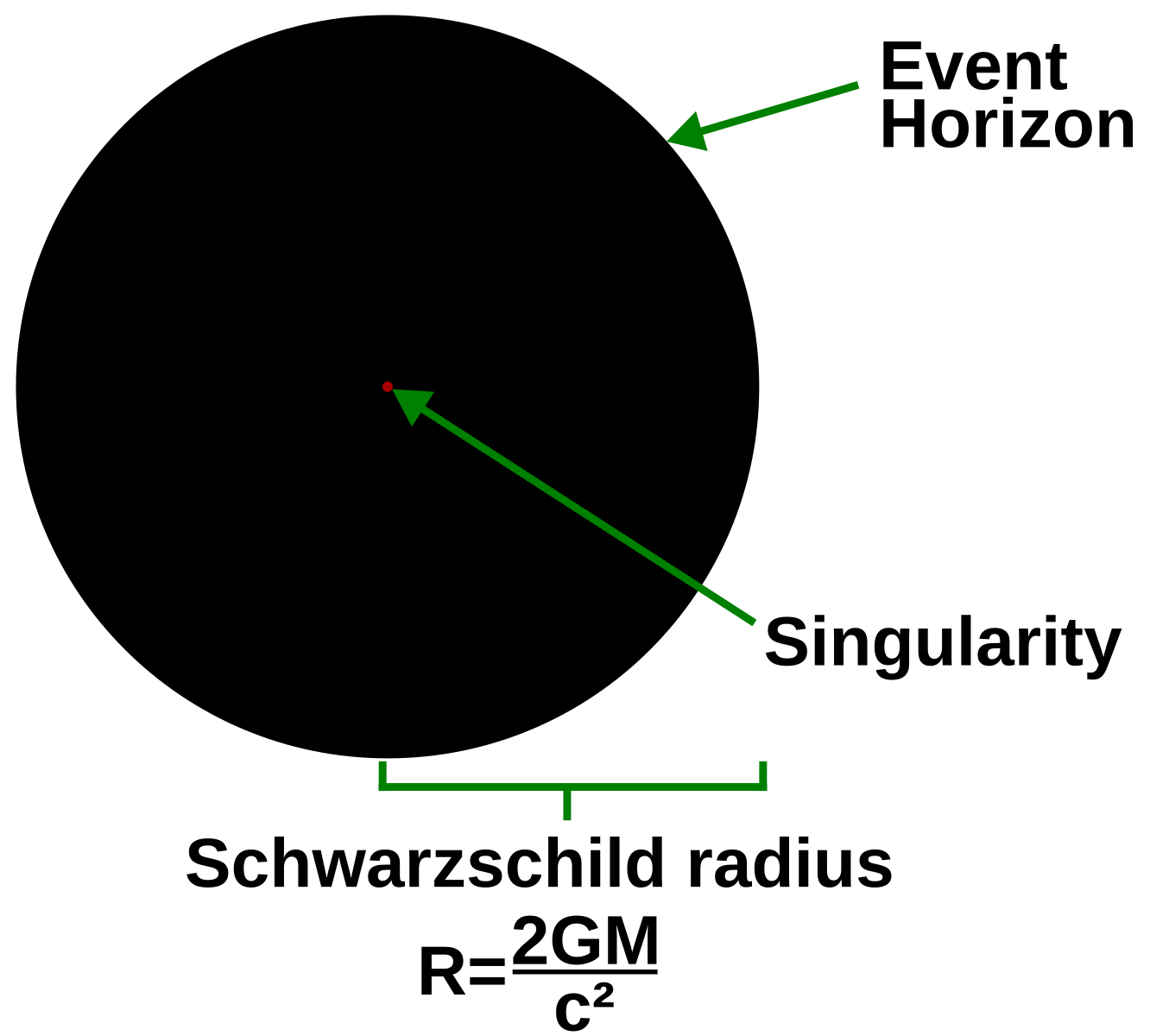
The surface at the Schwarzschild radius acts as an event horizon in a non-rotating body that fits inside this radius (although a rotating black hole operates slightly differently). The Schwarzschild radius of an object is proportional to its mass.. A black hole event horizon is teleological in nature, meaning that it is determined by future.
Researchers Can Now “See” Inside a Black Hole The Science Explorer

Merging the idea of escape velocity with the maximum speed with which matter can travel leads to the concepts of the Schwarzschild radius, black holes, and event horizons. If an object is sufficiently dense, it collapses upon itself and is surrounded by an event horizon from which nothing can escape. The name for such an object, "black hole.
Black Holes, Event Horizons and the Schwarzschild Radius YouTube

The Schwarzschild radius or the gravitational radius is a physical parameter in the Schwarzschild solution to Einstein's field equations that corresponds to the radius defining the event horizon of a Schwarzschild black hole.It is a characteristic radius associated with any quantity of mass. The Schwarzschild radius was named after the German astronomer Karl Schwarzschild, who calculated this.
Event Horizon Black Hole Diameter

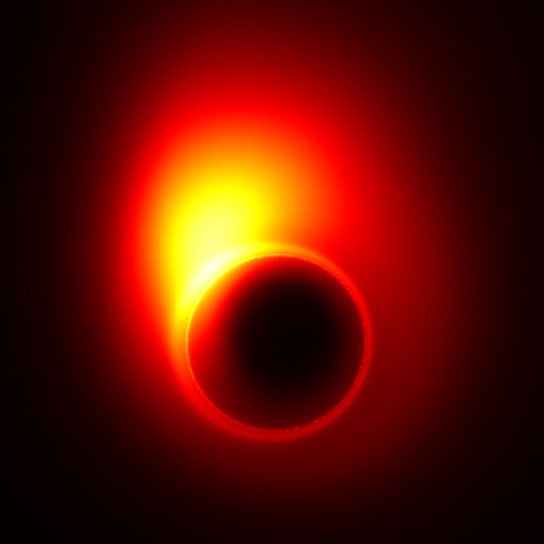
Using the Event Horizon Telescope, an international team of scientists has for the first time measured the radius of a black hole at the center of M87, a galaxy some 50 million light years from the Milky Way. The point of no return: In astronomy, it's known as a black hole — a region in space where the pull of gravity is so strong that.
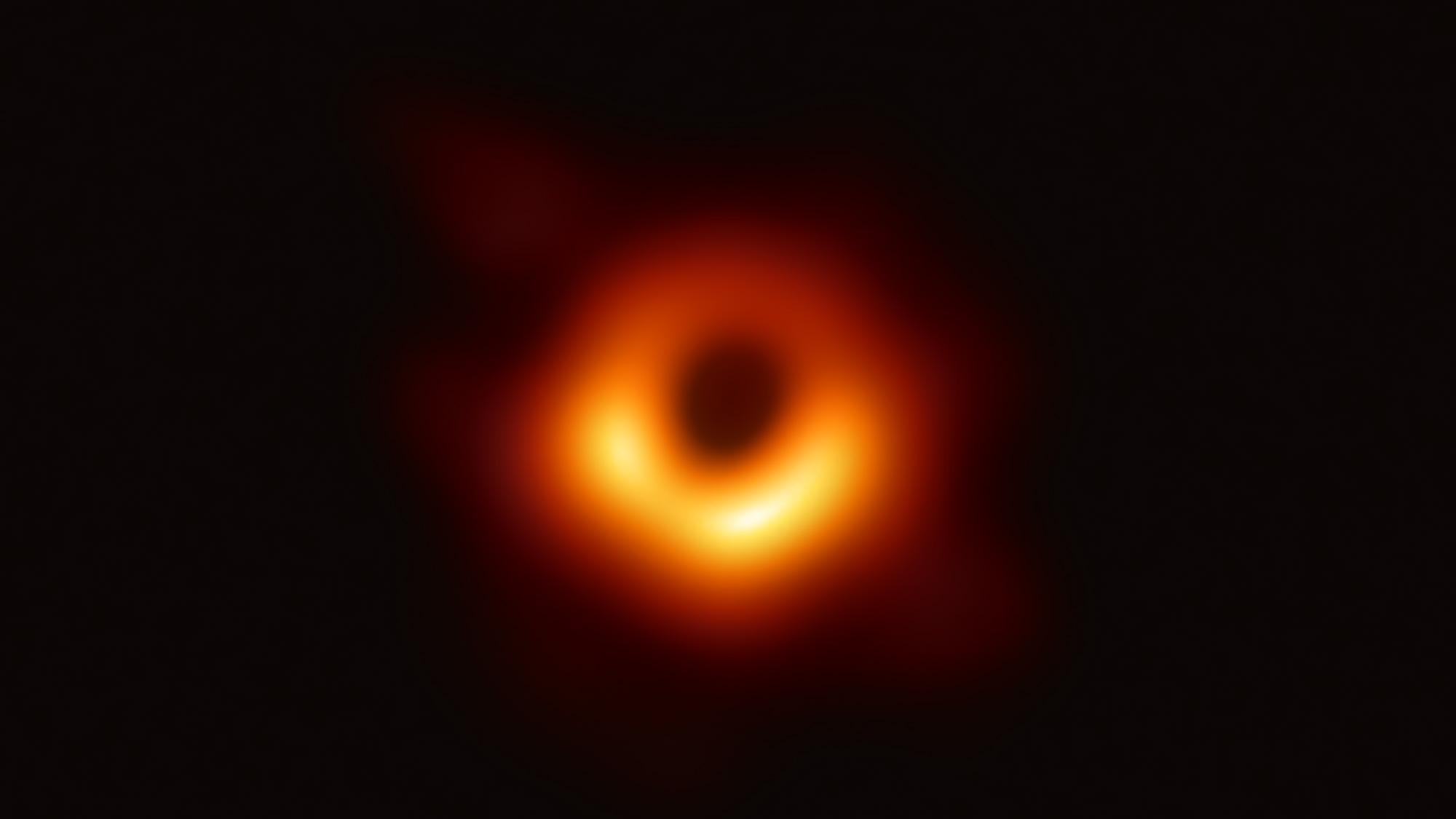
First Images of a Black Hole from the Event Horizon Telescope AAS Nova

The event horizon is the "point of no return" around the black hole. It is not a physical surface, but a sphere surrounding the black hole that marks where the escape velocity is equal to the speed of light. Its radius is the Schwarzschild radius mentioned earlier. One thing about the event horizon: once matter is inside it, that matter will.
Black Holes explained Astronomy Source

Black holes are massive objects that have become so dense that they collapse in on themselves under their own gravitational attraction. The Schwarzschild radius \(R_{S}\) is defined as the distance from a spherically symmetric mass distribution at which the escape velocity from the sphere is equal to the speed of light, i.e., it is the location of the event horizon.
Event Horizon Black Hole Diameter

The event horizon in a black hole is also called the Schwarzschild radius, after the physicist who first introduced this concept. For a non-rotating black hole, it depends only on the mass of the black hole, which makes this black hole event horizon/ Schwarzschild radius calculator very easy to use as it only needs one input parameter.
Scientists Measure the Radius of a Black Hole at the Center of M87

This phenomenon is thought to be the final fate of the more massive stars ( see black hole ). The Schwarzschild radius ( Rg) of an object of mass M is given by the following formula, in which G is the universal gravitational constant and c is the speed of light: Rg = 2 GM / c2. For a mass as small as a human being, the Schwarzschild radius is.
Rotating Black Hole Schwarzschild Radius Schwarzschild Metric Event
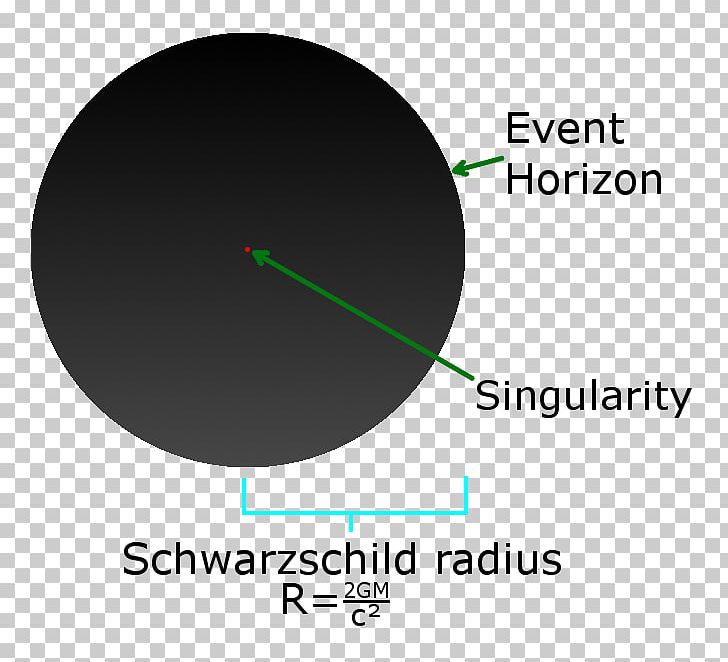
The size of a black hole, as determined by the radius of the event horizon, or Schwarzschild radius, is proportional to the mass, M, through = , where r s is the Schwarzschild radius and M ☉ is the mass of the Sun.
What Exactly Is a Black Hole Event Horizon (and What Happens There
The Schwarzschild black hole is characterized by a surrounding spherical boundary, called the event horizon, which is situated at the Schwarzschild radius (), often called the radius of a black hole. The boundary is not a physical surface, and a person who fell through the event horizon (before being torn apart by tidal forces) would not notice.
Black Hole Radii Wooster Physicists

The Schwarzschild radius is related to black holes. The distance between a static, non-rotating, and electrically neutral black hole's center and its edge of influence, called the event horizon.
Event Horizon, Singularity and Photon Sphere of a Black Hole Physics Feed
The mass gained by the black hole is the initial mass of the other object minus the mass that was converted into energy. The new mass of the black hole, together with the total energy released and the new event horizon radius, are computed and shown to you in the black hole collision calculator. Feel free to play around with it and try as many.
How Many Types of Black Holes Are There? Owlcation

event horizon, boundary marking the limits of a black hole.At the event horizon, the escape velocity is equal to the speed of light.Since general relativity states that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, nothing inside the event horizon can ever cross the boundary and escape beyond it, including light.Thus, nothing that enters a black hole can get out or can be observed from.
Event Horizon Telescope — A complete guide Space

Radius of the event horizon of a (non-spinning) black hole of mass )is the Schwarzschild radius! *= 2 &+!-Mass Schwarzschild Radius Sun (1& ⨀) 1.5 km Stellar mass black hole (10& ⨀) 15 km Stellar mass black hole (10/& ⨀) 1.5 x 106km 2 protons with energy 7TeV 10-50m The size of the event horizon (the Schwarzschild radius) depends on the.
This Is Why The Event Horizon Telescope Still Doesn’t Have An Image Of

The radius of the event horizon (proportional to the mass) is very small, only 30 kilometers for a non-spinning black hole with the mass of 10 Suns. Anything that passes beyond the event horizon is doomed to be crushed as it descends ever deeper into the gravitational well of the black hole.
Black hole images First look at Sagittarius A* at heart of Milky Way
An alternative method of measuring the volume of a black hole is to take the radius beyond which light can't escape, also commonly known as the Event horizon. Wikipedia has a great article on potential black hole sizes and masses, using the event horizon. Here's a few example values: