Differences Between R Squared and Adjusted R Squared Example and
Adjusted R Squared Equation Tessshebaylo

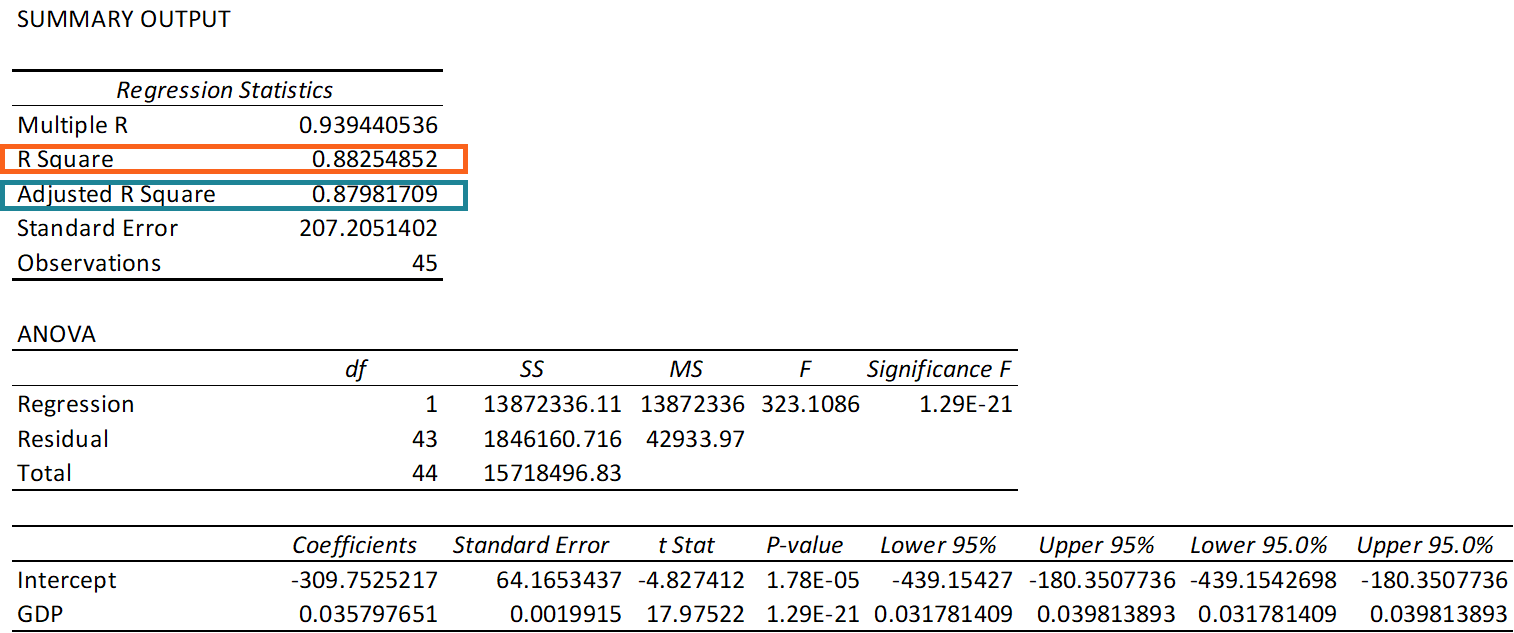
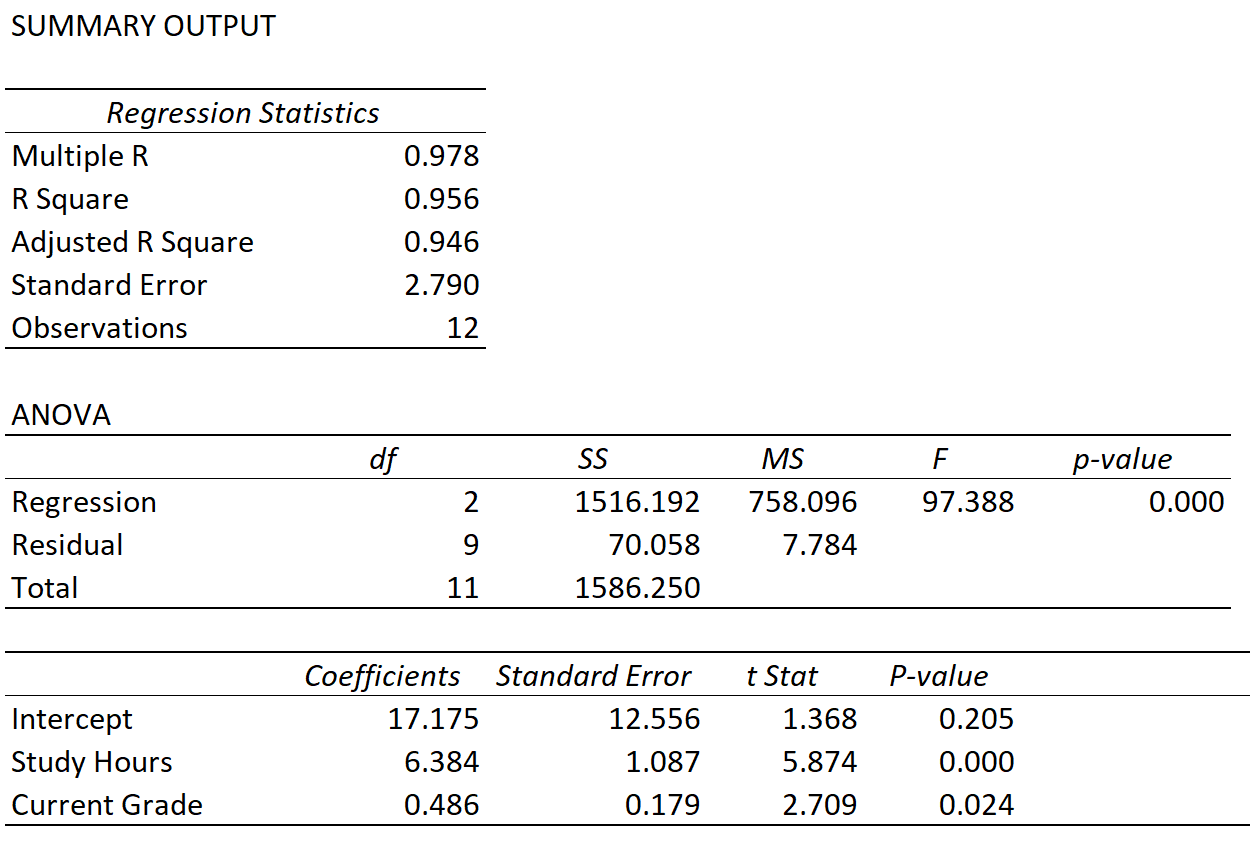
This represents the multiple correlation between the response variable and the two predictor variables. R Square: 0.956. This is calculated as (Multiple R)2 = (0.978)2 = 0.956. This tells us that 95.6% of the variation in exam scores can be explained by the number of hours spent studying by the student and their current grade in the course.
Difference between Rsquare and Adjusted RSquared

R-squared is a goodness-of-fit measure that tends to reward you for including too many independent variables in a regression model, and it doesn't provide any incentive to stop adding more. Adjusted R-squared and predicted R-squared use different approaches to help you fight that impulse to add too many. The protection that adjusted R-squared and predicted R-squared provide is critical.
Understanding R Squared From ExampleR Squared clearly explained YouTube
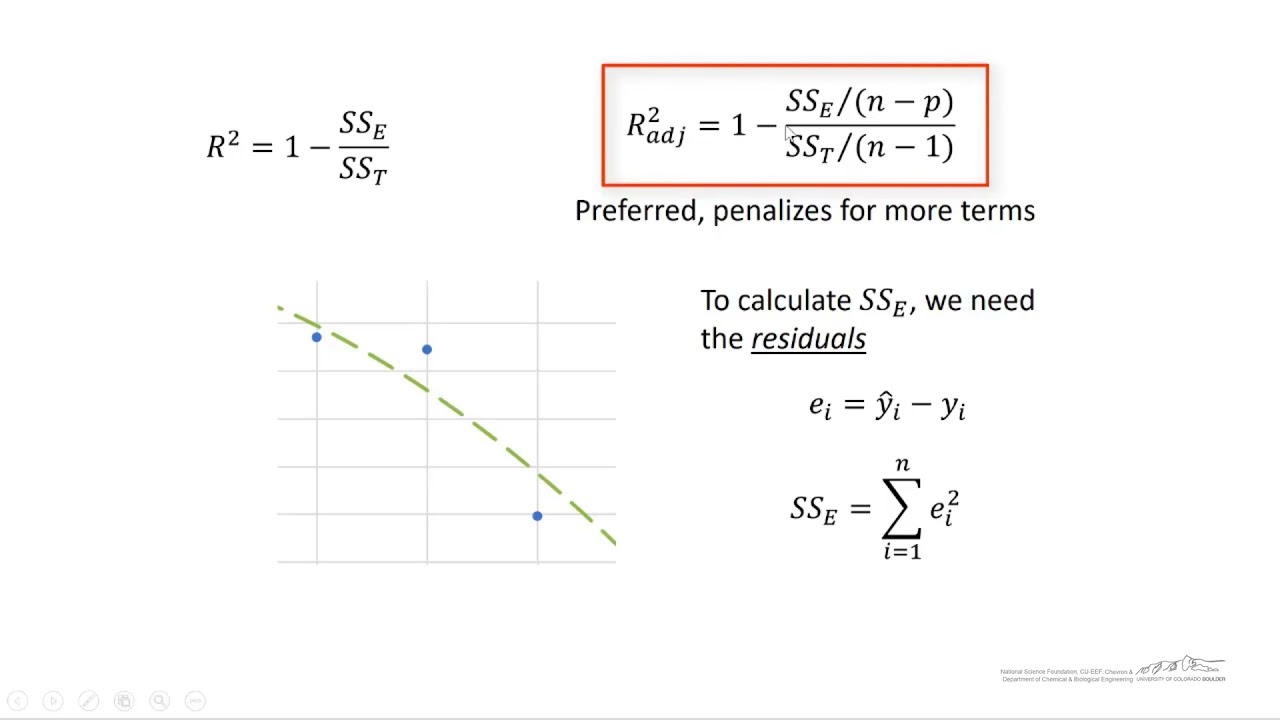
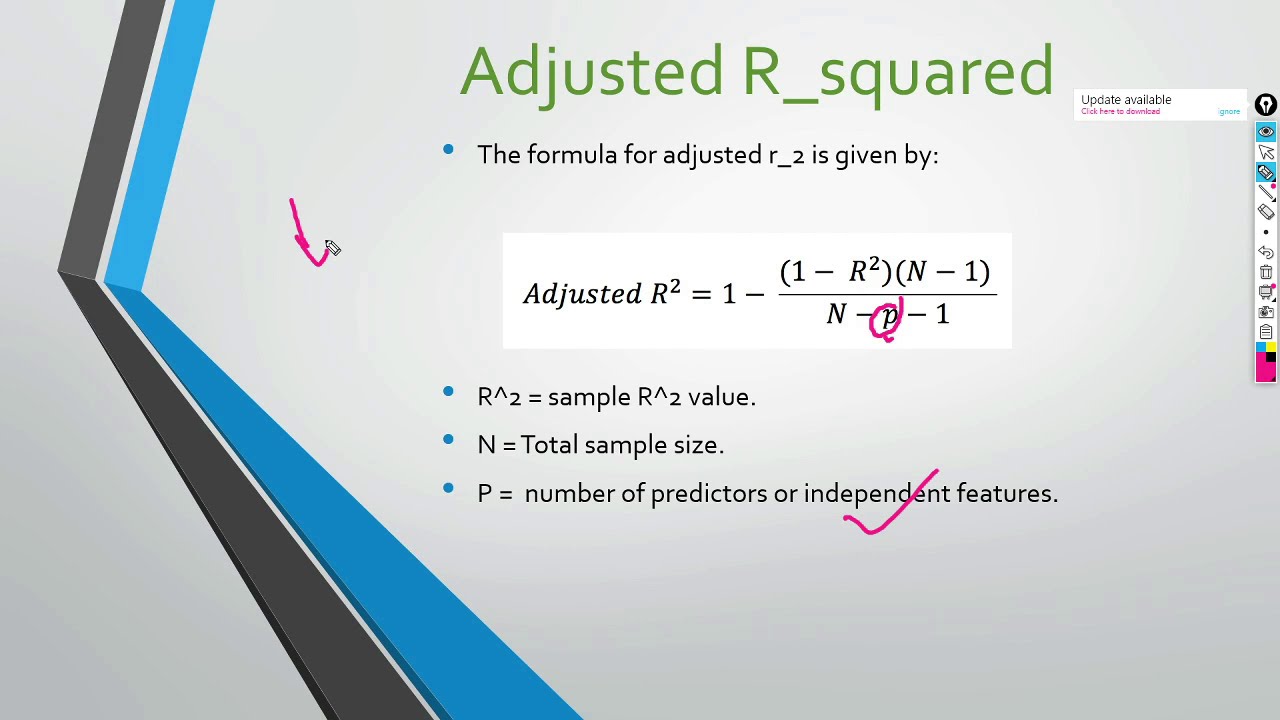
To answer your first question: if you have even a single predictor, the R2 R 2 and adj. R2 R 2 would be different. Check the adj. R2 R 2 formula below: R¯ = − ( −R) n − n − p − R ¯ = − ( − R) n − n − p −. You can see that having a single predictor ( p p) would change the denominator and the adj. R2 R 2. The difference.
Rsquared, Adjusted Rsquared and PseudoRsquared Time Series

Adjusted R² does just what is says: it adjusts the R² value. This adjustment is a penalty that is subtracted from R². The size of the penalty is based on the number of predictors and the sample size. If you add a predictor that is useful in predicting Y, the adjusted R² will increase because the penalty will be smaller than the R² increase.
RSquared Definition, Interpretation, Formula, How to Calculate
R-squared and Adjusted R-squared are valuable tools for assessing the quality of regression models, but they serve different purposes and are applied in distinct scenarios. R-squared provides a simple measure of goodness-of-fit and is suitable for quick assessments, model comparisons, and understanding the explanatory power of independent.
Adjusted Rsquared YouTube
R-squared and the adjusted R-squared both help investors measure the correlation between a mutual fund or portfolio with a stock index. Adjusted R-squared, a modified version of R-squared, adds.
How to get an Adjusted RSquare in Linear Regression Displayr Help
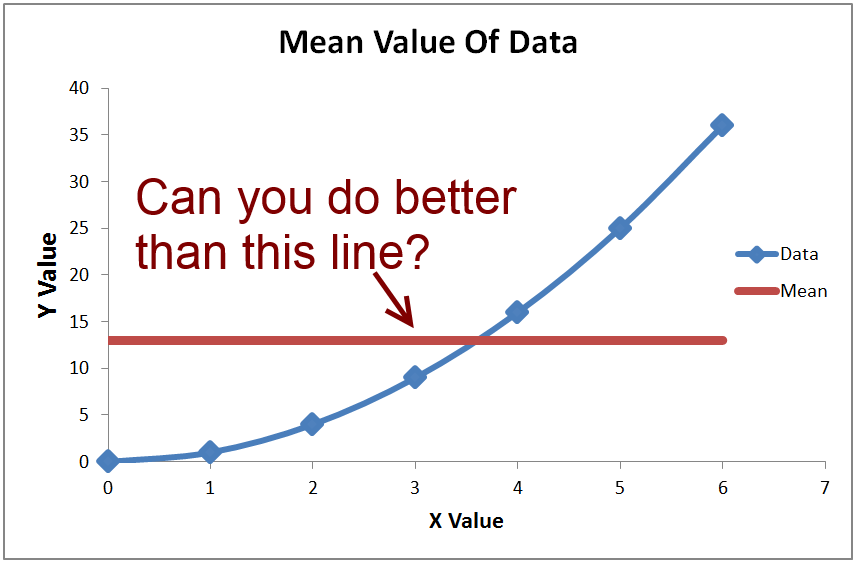
One of the most used and therefore misused measures in Regression Analysis is R² (pronounced R-squared). It's sometimes called by its long name: coefficient of determination and it's frequently confused with the coefficient of correlation r² . See it's getting baffling already! The technical definition of R² is that it is the proportion of variance in the response variable y that your.
Correlation vs Collinearity vs Multicollinearity QUANTIFYING HEALTH
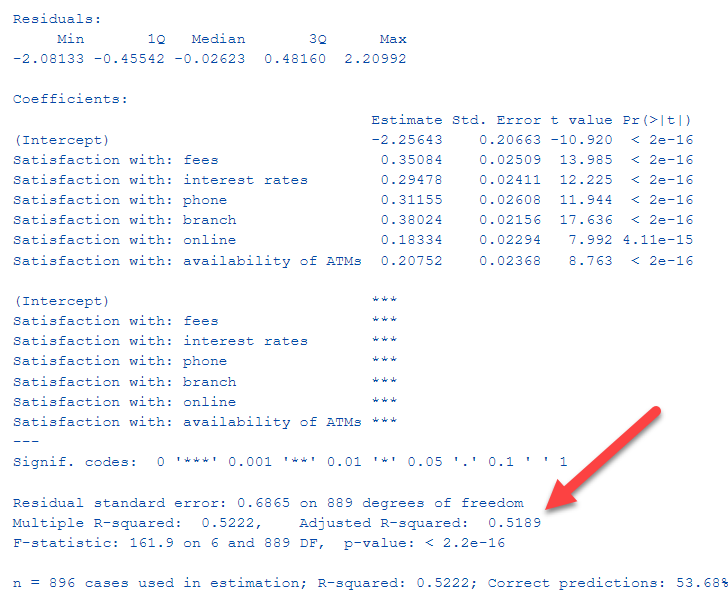
R^2 # 0.2347469. X X X X. the multiple R be thought of as the absolute value of the correlation coefficient (or the correlation coefficient without the negative sign)! The R-squared is simply the square of the multiple R. It can be through of as percentage of variation caused by the independent variable (s)
[Solved] What is the difference between Multiple 9to5Answer
The adjusted R-squared is. The adjusted R-squared adds a penalty for adding variables to the model that are uncorrelated with the variable your trying to explain. You can use it to test if a variable is relevant to the thing your trying to explain. Adjusted R-squared is R-squared with some divisions added to make it dependent on the number of.
XGBoost regression with poor accuracy KNIME Analytics Platform
Adjusted Rsquared controls against this increase, and adds penalties for the number of predictors in the model. Therefore it shows a balance between the most parsimonious model, and the best fitting model. Generally, if you have a large difference between your multiple and your adjusted Rsquared that indicates you may have overfit your model.
What Is R Squared On A Graph ZOHAL
Adjusted R-squared addresses a limitation of R-squared, especially in multiple regression (models with more than one independent variable). While R-squared tends to increase as more variables are added to the model (even if they don't improve the model significantly), Adjusted R-squared penalizes the addition of unnecessary variables.
what does r squared mean What is adjusted rsquare? what is a good
R-squared always increases when a new feature is added, while Adjusted R-squared increases only if the new feature improves the model more than expected by chance. Interpreting R-squared Values: An R-squared of 0 means the model does not explain any variance in the target.
Differences Between R Squared and Adjusted R Squared Example and

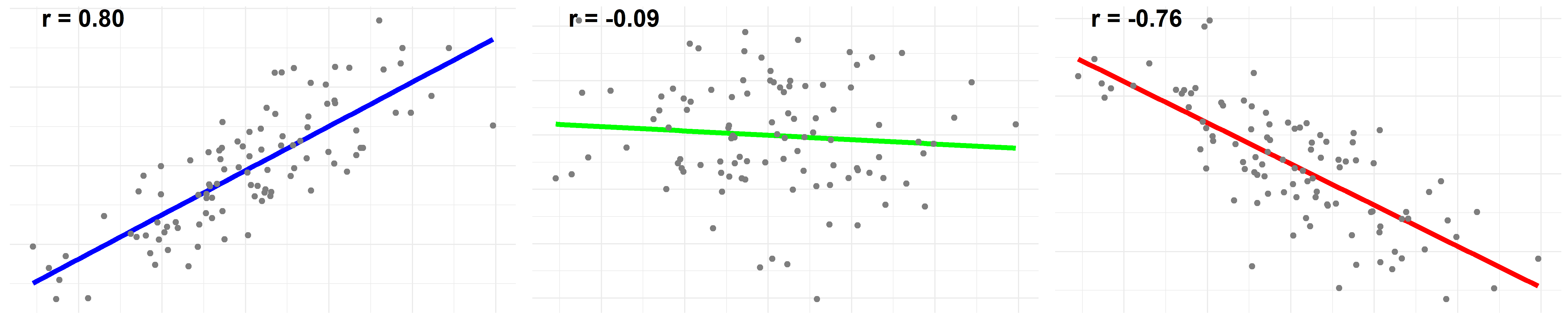
This chapter discusses some terms that are used in correlation analysis and linear regression. r is the correlation coefficient. It is also known as the "Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient", "PPMCC" or "PCC", or "Pearson's r". Multiple R is the "multiple correlation coefficient".
Несколько R против RSquared в чем разница?
The adjusted R-squared is a modified version of R-squared that has been adjusted for the number of predictors in the model. The adjusted R-squared increases only if the new term improves the model more than would be expected by chance. It decreases when a predictor improves the model by less than expected by chance. The adjusted R-squared can.
R vs R Squared Learn Top 8 Key difference with Comparision Table
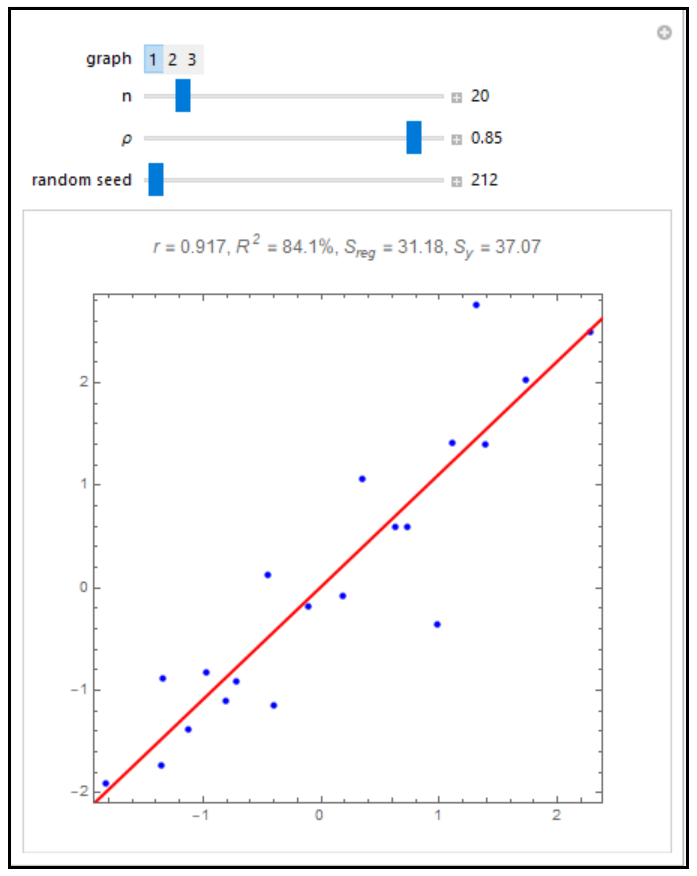
Let's first look at the 'Multiple R-squared'. This is an estimate of the population R squared value obtained by dividing the model sum of squares, as an estimate of the variability of the linear predictor, by the total sum of squares: where denotes the predicted value of and denotes the sample mean of Y. To check this, we can simulate a.
R and R squared YouTube

Multiple R: 0.978. This represents the multiple correlation between the response variable and the two predictor variables. R Square: 0.956. This is calculated as (Multiple R)2 = (0.978)2 = 0.956. This tells us that 95.6% of the variation in exam scores can be explained by the number of hours spent studying by the student and their current grade.